Introduction to Indoor Air Quality Solutions:
Indoor Air Quality Solutions become one of the most important aspects of modern living. As people spend more time Indoor Air Quality Solutions—working, studying, sleeping, and relaxing—the air inside homes, offices, and commercial buildings plays a major role in overall health and comfort. PoorIndoor Air Quality Solutions can contribute to allergies, fatigue, respiratory issues, and long-term health problems, even when the environment looks clean on the surface.
The challenge with Indoor Air Quality Solutions is that many of its threats are invisible. Pollutants such as dust, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), mold spores, bacteria, and fine particulate matter circulate freely without any obvious warning signs. Unlike outdoor pollution, which we can often see or smell, indoor pollution tends to build up slowly, making it easy to ignore until symptoms appear.
Indoor air quality solutions focus on identifying, controlling, and eliminating these hidden pollutants. They combine technology, smart building design, proper ventilation, and everyday habits that reduce contamination at the source. The goal is not just cleaner air, but healthier, more productive, and more comfortable indoor environments.
This article explores indoor air quality solutions in depth, from understanding common pollutants to implementing practical strategies at home and in professional spaces. Whether you are a homeowner, renter, facility manager, or simply someone who wants to breathe better, these insights will help you make informed decisions.
Understanding Indoor Air Quality and Its Impact
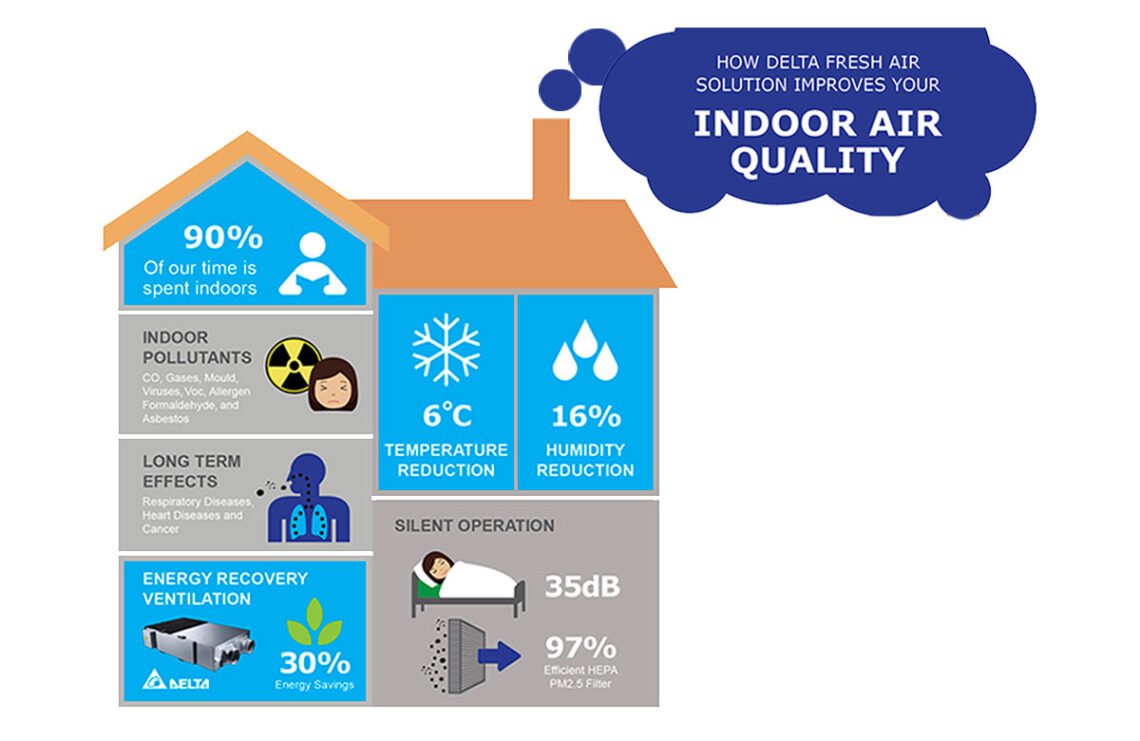
Indoor Air Quality Solutions refers to the condition of the air within buildings and enclosed spaces, particularly as it relates to the health and comfort of occupants. It is influenced by factors such as ventilation, humidity, temperature, and the presence of airborne contaminants. When air circulation is limited and pollutants accumulate, indoor environments can become far more polluted than the air outdoors.
Many people underestimate how much indoor air affects daily well-being. Headaches, eye irritation, dry skin, coughing, and difficulty concentrating are often linked to poor air quality. Over time, exposure to polluted indoor air can worsen asthma, trigger allergies, and increase the risk of chronic respiratory conditions, especially in children and the elderly.
Modern construction methods, while energy-efficient, often seal buildings tightly to prevent heat loss. While this improves energy savings, it also traps pollutants inside. Everyday items such as furniture, cleaning products, paints, carpets, and electronics release chemicals into the air, slowly degrading indoor air quality.
Understanding indoor air quality is the first step toward improvement. Once people recognize that indoor air can be actively managed and improved, it becomes easier to adopt effective solutions that protect long-term health and comfort.
Common Sources of Indoor Air Pollution
Indoor air pollution comes from a wide variety of sources, many of which are part of everyday life. Dust and pet dander are among the most common pollutants, accumulating on surfaces and becoming airborne through movement. These particles can irritate the respiratory system and trigger allergic reactions.
Chemical pollutants are another major concern. Volatile organic compounds are released by paints, adhesives, cleaning agents, air fresheners, and even new furniture. These chemicals can cause short-term discomfort such as dizziness and nausea, while long-term exposure may have more serious health consequences.
Biological pollutants also significantly affect indoor air quality. Mold spores thrive in damp environments, while bacteria and viruses spread easily in enclosed spaces with poor ventilation. Humidity levels that are too high or too low can worsen these issues by creating ideal conditions for microbial growth or drying out respiratory passages.
Combustion pollutants should not be overlooked. Gas stoves, fireplaces, candles, and tobacco smoke release carbon monoxide and fine particles into the air. Without proper ventilation, these pollutants can reach dangerous levels, making it essential to manage combustion sources carefully.
Ventilation as a Core Indoor Air Quality Solution
Ventilation is one of the most fundamental indoor air quality solutions available. It works by replacing stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air, reducing the concentration of pollutants inside. Proper ventilation helps control humidity, remove odors, and dilute airborne contaminants that accumulate over time.
Natural ventilation, such as opening windows and doors, is the simplest method. It can be highly effective in mild climates or during certain seasons. However, natural ventilation is not always reliable, especially in areas with outdoor pollution, extreme weather, or limited airflow.
Mechanical ventilation systems provide more consistent and controlled air exchange. Exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms remove moisture and pollutants directly at the source. Whole-house ventilation systems, including heat recovery ventilators, balance energy efficiency with air quality by bringing in fresh air while minimizing heat loss.
Effective ventilation requires thoughtful planning. Too little ventilation traps pollutants, while too much can increase energy costs and reduce comfort. When designed and maintained properly, ventilation systems form the backbone of a healthy indoor air environment.
Air Purification Technologies and Their Role
Air purification technologies play a vital role in modern indoor air quality solutions. These systems work by actively removing contaminants from the air rather than simply diluting them. They are especially useful in urban areas, allergy-prone households, and buildings with limited ventilation options.
High-efficiency particulate air filters are among the most widely used solutions. They are designed to capture fine particles such as dust, pollen, pet dander, and smoke. When installed in air purifiers or HVAC systems, these filters significantly reduce airborne allergens and improve overall air cleanliness.
Some air purifiers incorporate activated carbon filters, which are particularly effective at removing odors and chemical pollutants. These filters absorb gases and volatile organic compounds, making them ideal for spaces exposed to cleaning products, cooking fumes, or off-gassing materials.
Advanced air purification systems may also use ultraviolet light or ionization technology to neutralize bacteria and viruses. While these technologies can be effective, they should be selected carefully and used as part of a broader indoor air quality strategy rather than as standalone solutions.
Managing Humidity for Better Indoor Air
Humidity control is often overlooked, yet it plays a critical role in indoor air quality. Both high and low humidity levels can create problems that affect comfort and health. Maintaining balanced humidity helps reduce the growth of mold, bacteria, and dust mites while keeping respiratory systems comfortable.
High humidity creates an ideal environment for mold growth, which releases spores into the air. These spores can trigger allergies, asthma, and other respiratory conditions. Moisture buildup often occurs in bathrooms, kitchens, basements, and poorly ventilated areas.
Low humidity, on the other hand, can dry out skin, eyes, and nasal passages. It can also increase the spread of airborne viruses and cause static electricity buildup. Dry indoor air is especially common during winter months when heating systems are in use.
Indoor air quality solutions often include humidifiers or dehumidifiers, depending on the climate and building conditions. Monitoring humidity levels and keeping them within a healthy range improves comfort and supports cleaner, healthier air.
Source Control Strategies for Cleaner Indoor Air
Source control focuses on reducing or eliminating pollutants at their origin before they spread through indoor spaces. This approach is one of the most effective and cost-efficient indoor air quality solutions available. By addressing the source, it minimizes the need for complex filtration or ventilation systems.
Choosing low-emission materials is a key source control strategy. Paints, adhesives, furniture, and flooring products labeled as low-VOC release fewer harmful chemicals into the air. Making informed purchasing decisions can significantly reduce long-term indoor pollution.
Housekeeping practices also influence source control. Regular cleaning with gentle, non-toxic products reduces dust and chemical residue. Proper storage of chemicals and avoiding unnecessary use of air fresheners help limit airborne contaminants.
Behavioral changes play an important role as well. Avoiding indoor smoking, managing pets responsibly, and promptly fixing leaks or moisture issues all contribute to healthier indoor air. Small changes, when applied consistently, can make a noticeable difference.
Indoor Air Quality Solutions for Homes
Homes present unique indoor air quality challenges because they combine living, cooking, sleeping, and recreational activities in one space. Effective solutions must balance comfort, practicality, and affordability while addressing a wide range of pollutants.
Improving ventilation in homes often starts with simple steps such as using exhaust fans, opening windows when possible, and ensuring HVAC systems are well maintained. Regular filter replacement is one of the easiest yet most effective actions homeowners can take.
Air purifiers are particularly beneficial in bedrooms and living areas where people spend the most time. Choosing the right size and type of purifier ensures optimal performance without unnecessary energy use or noise.
Healthy indoor air habits, such as keeping humidity in check, minimizing clutter, and choosing safer cleaning products, reinforce technical solutions. Over time, these combined efforts create a healthier and more comfortable living environment.
Indoor Air Quality Solutions for Offices and Commercial Spaces
Offices and commercial buildings face different challenges compared to homes due to higher occupancy levels and longer operating hours. Poor indoor air quality in these environments can reduce productivity, increase absenteeism, and negatively affect employee morale.
Ventilation design is especially critical in commercial spaces. Fresh air intake must be sufficient to accommodate the number of occupants and the activities taking place. Regular maintenance ensures that ventilation systems continue to operate efficiently and safely.
Air filtration systems in offices often need to handle larger volumes of air and more diverse pollutants. Upgrading filters and integrating air purification technologies can significantly improve indoor air quality without disrupting daily operations.
Workplace policies also contribute to cleaner air. Encouraging good hygiene, managing indoor plants responsibly, and using low-emission office supplies help reduce pollution sources. When indoor air quality is prioritized, both health and performance benefit.
Monitoring and Maintaining Indoor Air Quality
Monitoring Indoor Air Quality Solutions is essential for maintaining long-term results. Without measurement, it is difficult to know whether solutions are working effectively or if new issues have emerged. Regular monitoring allows for proactive adjustments before problems escalate.
Indoor air quality monitors can track factors such as particulate matter, humidity, temperature, and chemical levels. These devices provide valuable insights and help identify patterns related to daily activities or seasonal changes.
Maintenance is just as important as monitoring. Filters must be replaced on schedule, ventilation systems cleaned, and humidity devices serviced regularly. Neglecting maintenance can reduce effectiveness and even worsen air quality over time.
A long-term commitment to indoor air quality ensures that improvements are sustained. By combining monitoring, maintenance, and smart habits, indoor environments remain healthy, comfortable, and safe year after year.
Conclusion:
Indoor air quality solutions are no longer optional luxuries; they are essential components of modern healthy living. As people become more aware of how indoor environments affect well-being, the demand for effective and practical solutions continues to grow.
From ventilation and air purification to humidity control and source reduction, improving indoor air quality requires a balanced and thoughtful approach. No single solution works in isolation, but when combined, these strategies create powerful results.
The benefits of clean indoor air extend beyond physical health. Improved focus, better sleep, higher productivity, and enhanced comfort all stem from healthier air. These advantages make indoor air quality investments worthwhile for homes and workplaces alike.
By understanding indoor air quality and applying proven solutions consistently, anyone can take control of their indoor environment. Cleaner air leads to better living, and better living starts with the air we breathe every day.